Grid-forming Inverter Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report, By Type (Micro-Inverter, String-Inverter, and Central-Inverter), By Power Rating (Below 10 KW, 10 - 50 KW, 50 - 100 KW, and Above 100 KW), By Application (Solar PV Plant, Wind Power Plant, and Energy Storage System), and Regional Forecast, 2026-2034
CURRENT AND PROJECTED MARKET SIZE OF THE GRID-FORMING INVERTER INDUSTRY?
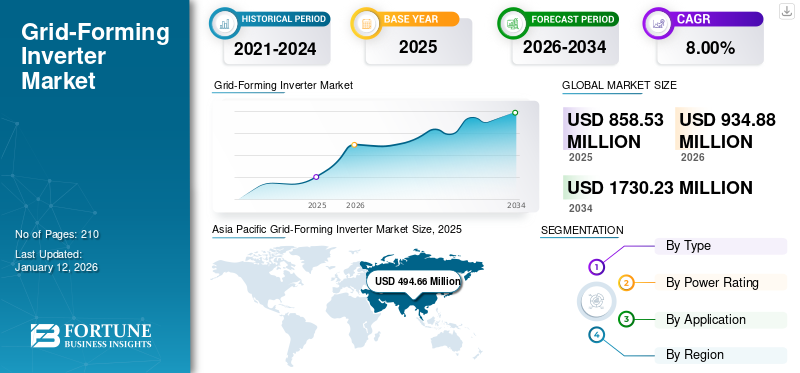
The global grid-forming inverter market size was valued at USD 858.53 million in 2025 and is projected to grow from USD 934.88 million in 2026 to USD 1,730.23 million by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 8.00% during the forecast period. Asia Pacific dominated the grid-forming inverter market with a market share of 57.62% in 2025.
A grid-forming inverter is a power electronic device that autonomously establishes and maintains grid parameters such as voltage and frequency, imitating the behavior of traditional synchronous generators. It plays a crucial role in integrating renewable energy sources such as solar and wind into the grid, ensuring stability during fluctuations, and enabling the creation of resilient micrograms. Grid inverters can adjust output power and voltage according to grid conditions and coordinate with other sources to balance supply and demand. The global push towards renewable energy sources technologies that can effectively integrate these variable sources into the grid while maintaining stability. Moreover, the increasing occurrence of extreme weather events and the significance of grid resilience have propelled the demand for GFIs. These inverters enable the creation of resilient microgrids capable of islanding from the main grid during emergencies, ensuring continuous power supply to critical infrastructure.
The global impact of COVID-19 on the market growth was moderate, as it hampered consumption in many end-use industries' growth due to supply chain disruption of services and technology and hindrance in activities due to social distancing norms. Furthermore, China and India are among the significant countries that manufacture and deploy grid-forming inverter technology. These countries have undergone various regional and national level shutdowns of residential, commercial, and industrial operations to contain the spread of this viral infection, which led to a fall in demand for grid-forming inverter market share.
WHAT ARE THE LATEST TRENDS SHAPING THE GRID-FORMING INVERTER MARKET?
Development of Innovative Technologies with Government Support Creates Commercial Opportunities
Advancements in power electronics and control algorithms have significantly improved the performance and efficiency of grid-forming inverter. These technological innovations have enhanced their ability to autonomously establish and maintain grid parameters, making them essential for integrating renewable energy sources into the grid. As renewable energy adoption continues to rise globally, the demand for grid-forming inverter is expected to increase proportionally.
Government support in the form of regulations, incentives, and funding has played a crucial role in promoting the growth of the grid-forming inverter market. For example, many countries have implemented renewable energy targets and policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. Governments offer incentives such as tax credits, subsidies, and feed-in tariffs to encourage the adoption of renewable energy technologies. Additionally, research and development grants and funding support innovative projects aimed at improving GFI technology and performance. The Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) mandates require utilities to produce or procure a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources. These mandates create a market demand for renewable energy technologies like grid-forming inverter as utilities seek to fulfill regulatory requirements.
Download Free sample to learn more about this report.
What are the key factors driving the growth of the grid-forming inverter market?
Adoption and Investment in Renewable Energy to Augment the Grid-forming Inverter to Fuel Market Growth
Renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power are gaining importance globally due to their environmental sustainability and decreasing costs. Governments, corporations, and individuals are increasingly investing in renewable energy projects to mitigate climate change and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. This surge in investment has led to a substantial increase in renewable energy capacity globally. For instance, The European Commission's REPowerEU policy aims to increase wind and solar power development, developing a surge in renewable energy investments of about USD 210 billion by 2027. This increased investment will drive demand for grid-forming inverter essential for integrating renewable energy into the grid efficiently. Additionally, the policy's focus on improving energy efficiency and expediting renewable energy deployment will further boost the demand for grid-forming inverter across residential, commercial, and industrial sectors.
As renewable energy installations continue to thrive, there is a growing need for advanced technologies to integrate these intermittent energy sources into the grid effectively. Grid-forming inverter play a critical role in this integration process by converting DC power generated by renewable sources into AC power compatible with the grid. Unlike traditional grid-following inverters, which rely on stable grid conditions to operate, grid-forming inverter can establish and maintain grid stability autonomously, making them vital in renewable energy systems. Moreover, advancements in energy storage technologies such as batteries complement grid-forming inverter by enabling the storage of excess renewable energy for later use, further enhancing grid stability and resiliency.
Regulatory Frameworks Promoting Grid Modernization and Growing Interest in Decentralized Energy Systems to Drive Market Growth
Government investments in smart grid infrastructure serves as a substance for grid modernization, aiming to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and resilience of electricity networks. Smart grids integrate advanced communication, control, and automation technologies to optimize energy management and facilitate the seamless integration of renewable energy sources, distributed generation, and energy storage systems. As governments worldwide prioritize the transition to cleaner, more sustainable energy systems, investments in smart grid initiatives have gained traction. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) found that with an ambitious goal of reducing carbon dioxide emissions to the grid by 2035, wind and solar power could provide up to 80% of production with a 100% clean electricity grid. As more investment-based resources are introduced, the grid must adapt to new types of energy technologies.
The growing interest in decentralized energy systems further strengthens the demand for grid-forming inverter, as these devices enable the seamless integration and control of distributed energy resources within the grid. Decentralized energy systems empower consumers to generate, store, and manage their electricity locally, reducing reliance on centralized power generation and enhancing energy independence. DOE funds research and innovation to support the integration of grid-type inverters into ever-growing and complex electric grids. For example, DOE awarded NREL about USD 3 million to create and validate advanced grid models that can simulate the dispatch and dynamic response of investment-based resources. NREL found that applying grid-shape adjustments across multiple inverters could help stabilize a 100% renewable energy system on Maui.
WHAT ARE THE KEY CHALLENGES LIMITING THE GROWTH OF THE GRID-FORMING INVERTER MARKET?
Availability of Alternative Traditional Grid-Following Inverter Impact To Hamper Market Growth
Traditional grid-following inverters have been widely utilized to integrate renewable energy sources into the grid. These inverters operate by synchronizing their output with the grid's voltage and frequency, adjusting their power generation according to grid conditions. While effective in many scenarios, traditional inverters have limitations, particularly in maintaining grid stability during periods of high renewable energy penetration or in isolated microgrid systems.
Compared to a grid-shaped inverter, grid-following inverters are easier and cheaper to implement. This can achieve faster power management response and avoid some of the technical challenges and regulatory hurdles that grid inverters face, such as synchronization, protection, coordination, and standards.
However, advancements in grid-following inverter technology have led to improved performance and capabilities, decreasing the distinction between traditional and grid-forming inverter. Modern grid-following inverters equipped with advanced control algorithms and communication protocols can provide some grid-forming functionalities, such as reactive power support and voltage regulation, albeit to a limited extent, hampering grid-forming inverter market growth.
Grid-Forming Inverter Market Segmentation Landscape
By Type Analysis
String-inverter Dominates the Market Since it is the Most Advanced and Highly Efficient Technology
Based on type, the market is segmented into micro-inverter, string-inverter, and central-inverter.
String-inverter holds a dominant with a share of 65.59% in 2026. The market since it is one of the most advanced inverter types and highly efficient technologies. String inverters are widely preferred due to their scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of installation. They are commonly used in photovoltaic (PV) solar systems where multiple solar panels are connected in series (or strings), allowing for flexibility in system design and installation. Moreover, string inverters offer high efficiency and reliability, making them suitable for various grid-forming applications, including residential, commercial, and utility-scale solar installations. Additionally, advancements in string inverter technology have led to the improved performance, grid integration capabilities, and compatibility with emerging grid standards, further solidifying their dominance in the market.
Central inverters are more commonly associated with utility-scale solar photovoltaic (PV) installations, where they convert the DC power generated by multiple solar panels into AC power for grid connection. However, central inverters typically operate in a grid-following mode, as they synchronize their output with the grid's voltage and frequency rather than autonomously establishing grid parameters like grid-forming inverter.
To know how our report can help streamline your business, Speak to Analyst
By Power Rating Analysis
Below 10 KW is Dominating the Market Due to its Rising Demand in Residential and Commercial Application
Based on power rating, the market is segmented into below 10 KW, 10 - 50 KW, 50 - 100 KW, and above 100 KW.
Below 10 KW holds a dominant with a share of 37.93% in 2026. Inverters with an output power of less than 10 kW are suitable for use in residential and commercial areas. The installation of photovoltaic systems in the residential sector is growing significantly globally. In addition to home inverters, string inverters, microinverters, and vehicle inverters also have an output voltage of less than 10 KW.
10 - 50 KW holds the second major share in the global market after below 10 KW. With a wide range of applications, including residential, commercial, and small-scale industrial projects, where energy demand falls within this power range, the installations in this power range often represent mid-sized solar PV systems or microgrids, which are increasingly popular for decentralized energy generation and grid resilience.
By Application Analysis
Solar PV Plants Holds a Dominant Share Due to the High Renewable Energy Penetration and Development
Based on end-user, the market is segmented into solar PV plants, wind power plants, and energy storage systems.
Solar PV plants hold a dominant share of 70.20% in 2026, the market driven by environmental concerns and the need to transition to cleaner energy sources. Solar PV technology has emerged as a frontrunner in this transition due to its abundant availability, scalability, and declining costs. Continuous advancements in solar PV technology, including improvements in efficiency and durability, have made solar PV plants increasingly competitive compared to conventional energy sources.
The wind power plant segment is the second most dominant segment after the solar PV plant due to supportive government policies, incentives, and subsidies that have encouraged the development of renewable projects, further boosting their market share. Solar energy and wind energy also offer advantages such as rapid deployment, low operating costs, and minimal environmental impact, making them a preferred choice for energy generation.
WHAT ARE THE MARKET DYNAMICS AND GROWTH PROSPECTS BY REGION?
The market has been studied geographically across five main regions: North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific Grid-Forming Inverter Market Size, 2025
To get more information on the regional analysis of this market, Download Free sample
Globally, Asia Pacific dominates the grid-forming inverter market share. The region is experiencing rapid industrialization and urbanization, leading to a substantial increase in energy demand, with the Asia Pacific market valued at USD 494.66 million in 2025. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea have made significant investments in renewable energy infrastructure, including solar and wind power projects. The Japan market is projected to reach USD 54.2 Million by 2026, the China market is projected to reach USD 327.83 Million by 2026, and the India market is projected to reach USD 71.18 Million by 2026. As a result, there is a growing focus on increasing grid reliability, stability, and resilience, driving the adoption of grid-forming inverter to support the integration of renewable energy sources and improve grid performance. The U.S. grid-forming inverter market is projected to experience significant growth, reaching an estimated value of USD 301.67 million by 2032.
North America
North America is the second leading region in the market. The amount of North American regional electricity generated by solar and wind power has increased dramatically over the last decade. U.S. electricity is now coming from renewable sources. Grid-forming inverter will likely play a large role in getting the energy safely into the power grid. The US Department of Energy is providing USD 25 million in funding to get more grid-shaped inverters into the US power system. The alliance, known as UNIFI, is the Universal Interoperability of grid-shaped Inverters, with continuous investment market dents to grow. The U.S. market is projected to reach USD 180.33 Million by 2026.
Europe
Europe has witnessed a substantial increase in renewable energy adoption in recent years. This includes the deployment of solar, wind power, and energy storage projects across various countries. Germany, a leader in renewable energy adoption, has implemented ambitious renewable energy goals, driving the deployment of grid-forming inverter to integrate large-scale solar and wind projects into the grid. The U.K. is also investing in five new projects, including a 300-megawatt power station in Scotland to be completed in 2024. The UK market is projected to reach USD 23.25 Million by 2026, while the Germany market is projected to reach USD 31.48 Million by 2026.
Latin America and Middle East & Africa
Latin America and Middle East & Africa markets are leading predominantly due to constant investment in smart grid and renewable technology.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Market Players Focusing on Expanding their Product Lines and Utilize its Channel on the Industry
The global grid-forming inverter market is highly fragmented, with large and some medium-scale regional players delivering a wide range of products at local and country levels across the value chain. Numerous companies are actively operating across different countries to cater to the specific demands of the customers.
SMA Solar Technology is expected to account for a significant market share owing to its extensive product portfolio, strong brand value, and continuous new project and technology development. Furthermore, the company is also focused on enhancing its sales, distribution, and marketing channels through partnerships with different local associates to fortify its product reach across the globe.
List of Key Companies Profiled:
- SMA Solar Technology (Germany)
- General Electric (U.S.)
- Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. (China)
- Gamesa Electric (Spain)
- SunGarner (India)
- Toshiba Corporation (Japan)
- AGL Energy (Australia)
- KACO new energy GmbH (Germany)
- Sungrow (China)
- Portland General Electric (U.S.)
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS IN THE GRID-FORMING INVERTER MARKET::
- December 2023 – AGL has started construction of a 50 MW/100 MWh large-scale Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) facility with an advanced grid-forming inverter at 74-76 Pinnacles Place, Broken Hill. The project will support Broken Hill's reliable electricity supply in the event of line failures and provide effective grid support to the region. The project also provides storage and compression capacity for the National Energy Market (NEM) and additional services to support grid stability.
- July 2023 – Gamesa introduces a new central inverter with grid-forming capabilities. According to Gamesa, its latest hybrid iteration of the Proteus inverter is compatible with large-scale battery systems and is capable of operating in both grid-following and grid-forming modes. This product offers scalability and can deliver up to 5.6 MVA of battery discharge power at 40 C and a voltage of 1,300 V, with an impressive efficiency rating of 99%.
- March 2023 – KACO New Energy GmbH, Infineon Technologies AG, and the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE have collaborated in the Stabil project to examine the potential stress factors expected to impact a grid-forming PV inverter within the future power grid. The objective is to translate these insights into an enhanced and resilient hardware design for the upcoming grid-forming PV inverter development.
- May 2023 – Portland General Electric has demonstrated its grid-forming inverter at the Wheatridge Renewable Energy Facility in Oregon, marking North America's first energy center to integrate wind, solar, and energy storage systems within a single location.
- August 2022 – Toshiba developed a grid-forming inverter for implementation in microgrid settings. The inverter underwent testing within a simulated microgrid environment characterized by a grid frequency of 50 Hz, a renewable energy penetration rate of 40%, and the integration of five battery units, each rated at 20 kW/14.9 kWh. Additionally, the system is comprised of a diesel synchronous generator boasting a capacity of 125 kVA, along with two load banks that enable adjustments to the power load.
REPORT COVERAGE
The report provides a detailed analysis of the market and focuses on key aspects such as leading companies, product/service types, and leading applications of the product. Besides, the report offers insights into the market trends and highlights key industry developments. In addition to the factors above, the report encompasses several factors that contributed to the growth of the market in recent years.
Request for Customization to gain extensive market insights.
REPORT SCOPE & SEGMENTATION
|
ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
|
Study Period |
2021-2034 |
|
Base Year |
2025 |
|
Forecast Period |
2026-2034 |
|
Historical Period |
2021-2025 |
|
Growth Rate |
CAGR of 8.00% from 2026 to 2034 |
|
Unit |
Value (USD Million) |
|
Segmentation |
By Type, By Power Rating, By Application, and By Region |
|
Segmentation |
By Type
|
|
By Power Rating
|
|
|
By Application
|
|
|
By Region
|
Frequently Asked Questions
As per the Fortune Business Insights study, the market size was USD 858.53 million in 2025.
The market is likely to grow at a CAGR of 8.00% over the forecast period.
The string-inverter segment leads the market due to the development of grid-forming inverter globally.
The Asia Pacific market size stood at USD 494.66 million in 2025.
Adoption and investment in renewable energy and regulatory frameworks promoting grid modernization and growing interest in decentralized energy systems.
Some of the top players in the market are SMA Solar Technology, General Electric, and Games Electric.
The global market size is expected to reach 1,730.23 million by 2034.
Related Reports
-
US +1 833 909 2966 ( Toll Free )
-
Get In Touch With Us