Space In-Orbit Refueling Market Size, Share & Industry Analysis, By Propellant (Chemical Propellants and Electric Propellants), By Operation (Refueling, Replenishment, Resupply, and Maintenance), By Platform (Satellites, Space Stations, and Space Exploration Probes), and Regional Forecast, 2024–2032
KEY MARKET INSIGHTS
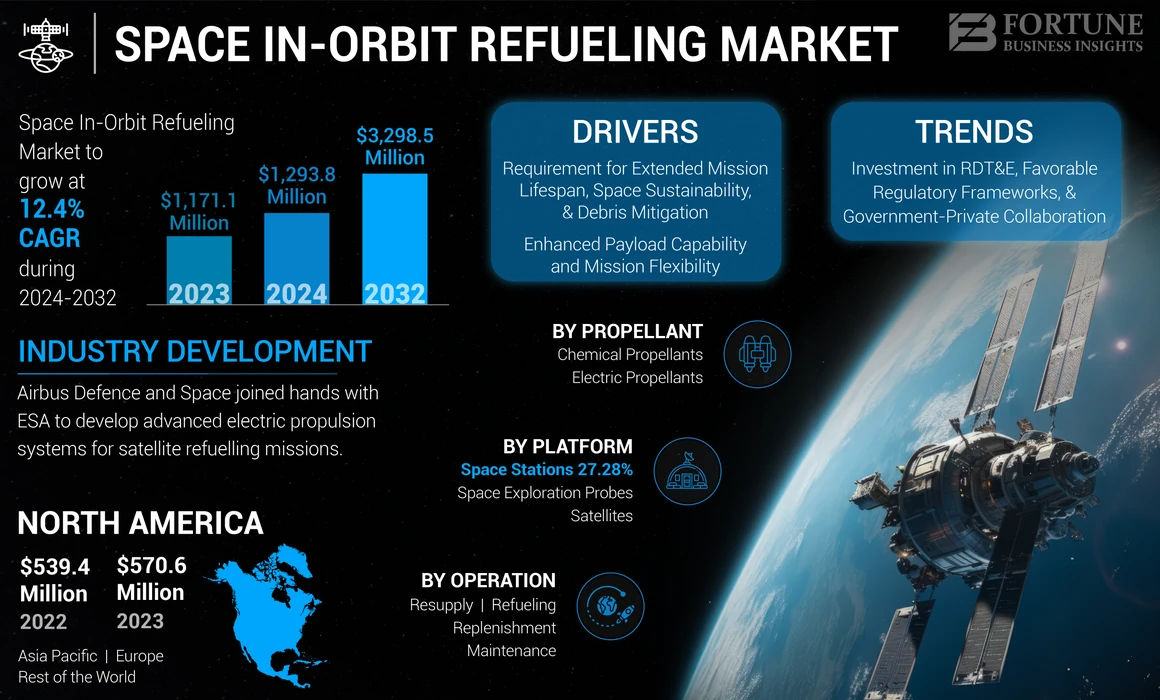
The global space in-orbit refueling market size was valued at USD 1,171.1 million in 2023 and is projected to grow from USD 1,293.8 million in 2024 and reach USD 3,298.5 million by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 12.4% during the forecast period. North America dominated the space in-orbit refueling market with a market share of 48.72% in 2023.
From an economic standpoint, incorporating refueling capabilities into satellite design and mission planning offers significant long-term benefits. It enables organizations to amortize costs over extended mission durations, enhancing return on investment and maximizing the utility of space assets. Furthermore, the reduced need for frequent satellite replacements translates into lower overall mission costs and improved financial efficiency. Additionally, innovations include the development of refueling vehicles and interfaces, such as Northrop Grumman's Passive Refueling Module (PRM), which has been selected as the preferred refueling solution interface standard by Space Mobility Systems Command.
The COVID-19 pandemic impacted the global space in-orbit refueling market. The pandemic caused supply chain disruptions and delays in the development and testing of in-orbit refueling technologies. Economic uncertainty led to some delays in investment and adoption of in-orbit refueling services by satellite operators. However, with the growing demand for satellite services such as earth observation, communication, and navigation, the need for in-orbit refueling to extend satellite lifespans has increased.
GLOBAL SPACE IN-ORBIT REFUELING MARKET KEY TAKEAWAYS
Market Size & Forecast:
- 2023 Market Size: USD 1,171.1 million
- 2024 Market Size: USD 1,293.8 million
- 2032 Forecast Market Size: USD 3,298.5 million
- CAGR: 12.4% from 2024–2032
Market Share:
- North America dominated the market with a 48.72% share in 2023, valued at USD 570.6 million.
- By propellant, Chemical Propellants held the largest share in 2023; Electric Propellants are projected to grow at the highest CAGR.
Key Country Highlights:
- U.S.: Home to key players including Northrop Grumman, Orbit Fab, and Maxar Technologies; significant public-private partnerships and R&D funding.
- Japan: Astroscale leads regional innovation; partnered with JAXA for debris removal and refueling solutions.
- Canada: Obruta Space Solutions active in autonomous servicing missions.
- Italy: D-Orbit SpA involved in orbital transport and servicing missions.
Space In-Orbit Refueling Market Trends
Investment in RDT&E, Favorable Regulatory Frameworks, and Government-Private Collaboration to Drive Market Growth
Investment in research, development, testing, and evaluation (RDT&E), coupled with the establishment of favorable regulatory frameworks and enhanced government-private collaboration, is poised to catalyze significant market growth in the long term. North America witnessed space in-orbit refueling market growth from USD 539.4 Million in 2022 to USD 570.6 Million in 2023.
Central to this growth is the substantial investment in RDT&E initiatives aimed at advancing technologies critical to space exploration and satellite operations. Companies and government agencies are channeling resources into developing innovative propulsion systems, autonomous navigation technologies, and sustainable in-space operations, such as satellite refueling and resource utilization. These investments drive technological advancements and foster a competitive landscape where companies developing refueling services strive to push the boundaries of what's possible in space.
The establishment of favorable regulatory frameworks further accelerates market growth by providing clear guidelines and standards for emerging space operations. Regulatory bodies are increasingly adapting to the dynamic nature of space operations, ensuring safety, sustainability, and equitable access to space resources. Clear and predictable regulations reduce uncertainties for investors and operators, encouraging greater participation and innovation in the sector.
Download Free sample to learn more about this report.
Space In-Orbit Refueling Market Growth Factors
Requirement for Extended Mission Lifespan, Space Sustainability, and Debris Mitigation to Propel Market Expansion
The need for an extended mission lifespan, coupled with initiatives for space sustainability and debris mitigation, has emerged as a pivotal force driving advancements in space technology and market dynamics. Traditionally, the operational life of satellites and spacecraft has been limited by their finite fuel capacity. Once depleted, these assets either cease to function effectively or contribute to the growing problem of space debris.
Refueling technology presents a transformative solution by extending the operational longevity of spacecraft. This capability enhances mission flexibility and offers substantial cost savings. Instead of prematurely decommissioning satellites due to fuel exhaustion, refueling allows them to continue performing critical tasks such as communications, Earth observation, and scientific research. By effectively doubling or tripling mission durations, refueling mitigates the need for launching costly replacement satellites, optimizing resource allocation, and reducing overall mission costs.
Moreover, refueling plays a crucial role in space sustainability efforts. Maintaining operational satellites rather than allowing them to become defunct or contribute to space debris minimizes the environmental impact of space activities. Space agencies and commercial entities increasingly recognize the importance of integrating sustainable practices into their operations. Refueling aligns with these sustainability goals and supports international efforts to mitigate space debris, ensuring safer and more sustainable orbits for future generations of satellites and spacecraft.
Enhanced Payload Capability and Mission Flexibility to Drive Market Growth
By replenishing fuel reserves in space, missions can be equipped with larger payloads and more advanced scientific instruments. This flexibility enhances the scientific and commercial potential of missions and maximizes the return on investment for satellite operators and space agencies.
Satellites can now be outfitted with additional sensors, communications equipment, or extended operational capabilities without compromising mission objectives. This capability is crucial for satellite constellations, Earth observation missions, and deep space probes, enabling a new era of exploration and discovery.
In-space refueling opens up unprecedented opportunities for deep space exploration. As humanity sets its sights on destinations such as Mars, the ability to refuel spacecraft en route becomes a strategic advantage. This approach reduces reliance on exceptionally powerful and costly launch vehicles, thereby streamlining mission architectures and lowering overall mission costs.
- For instance, SpaceX's Starship program exemplifies this paradigm shift by integrating refueling port capabilities into its design from the outset. The program envisions multiple refuelings to support ambitious missions such as crewed lunar landings under NASA's Artemis program. This capability extends mission durations and enhances the safety and feasibility of prolonged human presence in space.
RESTRAINING FACTORS
Technical Complexity and Reliability Issues to Hinder Market Growth
Balancing the benefits of extending satellite lifespans with the associated costs is a critical challenge that influences the trajectory of the satellite industry. Extending satellite missions can enhance operational efficiency, improve data continuity, and reduce launch frequency. However, it also introduces significant economic and technical considerations that can potentially hinder space in-orbit refueling market growth.
The primary benefit of extending satellite lifespans lies in maximizing the return on investment through prolonged operational periods. Satellites are costly to design, build, and launch, so extending their operational period allows operators to amortize these initial investments over a longer timeframe. This, in turn, can lead to lower per-year operational costs and increased revenue generation throughout the satellite's extended mission. Moreover, longer mission lifespans enhance the reliability and continuity of satellite services, benefiting users in sectors such as telecommunications, Earth observation, and scientific research.
However, extending satellite lifespans presents challenges. As satellites age, they encounter more technical complexities, requiring increased maintenance, software updates, and occasional hardware replacements to ensure continued functionality. The risk of technical failures and operational anomalies may increase with extended mission durations, which could potentially affect service reliability and customer satisfaction.
Space In-Orbit Refueling Market Segmentation Analysis
By Propellant Analysis
Rising space missions Creating Demand for increased payload capabilities to drive the Growth for Chemical Propellants
By propellant, the market is categorized into chemical propellants and electric propellants.
The chemical propellants segment dominated the global space in-orbit refueling market share in 2023. The segment accounted for the majority market share in 2023 and, is anticipated to grow at a moderate growth rate during the forecast period. Expanding satellite deployments, rise in space exploration missions, continued innovation, and investment in chemical propulsion technologies are the factors driving the segment growth during the forecast period.
- For instance, in July 2022, Eta Space announced the development of advanced cryogenic systems for its LOXSAT technology demonstration satellite. This satellite is designed to test critical cryogenic fluid management (CFM) technologies in Earth’s orbit for fluids such as liquid oxygen.
The electric propellants segment is estimated to grow significantly during the forecast period, with the highest anticipated CAGR. High demand for high specific impulse, reduction in propellant mass requirements, and increased payload capabilities are some of the factors driving the market growth.
- For instance, in July 2022, NASA awarded a contract to Aerojet Rocketdyne to develop next-generation ion propulsion systems for future in-orbit refueling missions. The contract focused on enhancing thruster performance and reliability to support NASA's Artemis program and lunar exploration objectives.
By Operation Analysis
Refueling Segment Held the Key Share due to Increasing Demand For Mission Extension Services
Based on operation, the market is fragmented into refueling, replenishment, resupply, and maintenance.
The refueling segment dominated the global space in-orbit refueling market in 2023, driven by the growing demand for mission extension, sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and mission flexibility.
- For instance, in June 2023, Northrop Grumman successfully completed a refueling mission using its Mission Extension Vehicle (MEV) to replenish the fuel of a client satellite in geostationary orbit. This milestone demonstrates the operational readiness and reliability of in-orbit refueling technology.
The maintenance segment is estimated to grow significantly during the forecast period. Growing demand for inactive satellites with expended propellants which accounts for 85% of satellite debris for extending lifespan and re-tasking assets for cost effectivity has been driving the segmental market growth during the forecast period.
- For instance, in April 2023, Airbus Defense and Space announced a partnership with the European Space Agency (ESA) to develop a new generation of satellite servicing vehicles capable of refueling and repairing satellites in orbit. This initiative aimed to advance European capabilities in space maintenance and sustainability.
By Platform Analysis
To know how our report can help streamline your business, Speak to Analyst
Growing satellites for orbit refueling will facilitate the demand for satellite platform market Segment
By platform, the market is divided into satellites, space stations, and space exploration probes.
The satellites segment dominated the global space in-orbit refueling market in 2023 and is anticipated to grow at a significant growth rate during the forecast period. Factors driving this growth include the need for orbital adjustments, maintaining optimal orbits, and managing complex mission profiles, such as station keeping, inclination changes, and orbital transfers.
- For instance, in March 2023, Astroscale announced plans to develop a satellite servicing vehicle capable of refueling and servicing multiple satellites in orbit. The initiative aimed to provide comprehensive satellite maintenance solutions and support sustainability efforts in space.
The space stations segment is estimated to grow at the highest growth rate during the forecast period. Growing demand for space stations to sustain extended missions by replenishing essential resources, such as propellants and life support systems, is one of the factor for the growth of the segment during the forecast period. The space stations segment is expected to hold a 27.28% share in 2023.
- For instance, in October 2023, NASA and SpaceX collaborated on a project to develop in-orbit refueling capabilities for the International Space Station (ISS). The initiative aimed to enhance the sustainability and operational capabilities of the ISS by enabling regular refueling missions to extend its operational life and support future exploration missions.
REGIONAL INSIGHTS
Based on geography, the space in-orbit refueling market is divided into regions: North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and rest of the world.
North America Space In-Orbit Refueling Market Size, 2023 (USD Million)
To get more information on the regional analysis of this market, Download Free sample
North America accounted for the largest share and accounted for USD 570.6 million in 2023, and is likely to remain dominant throughout the forecast period. Key factors driving this growth include advanced technological capabilities, strategic partnerships and collaborations between North American space agencies and private companies for satellite servicing, refueling, and space exploration missions. Additionally, the growth of the commercial space industry and government support and funding contribute to market growth in the North America. The region boasts advanced capabilities in spacecraft design, propulsion systems, and robotics, which are crucial for the development and implementation of in-orbit refueling technologies. These partnerships drive technological advancements and foster a conducive environment for the growth of in-orbit refueling capabilities.
The Asia Pacific region held a significant market share in 2023 and is estimated to be the fastest-growing region during the forecast period. Emerging space programs, commercial space industry growth, the need for in-orbit refueling capabilities to support long-duration missions, and collaborations between Asian countries and international partners are key factors driving the segment’s growth.
KEY INDUSTRY PLAYERS
Key Players Adapt Strategies to Ensure Market Survival by Expanding Service Portfolio
The space in-orbit refueling market is relatively fragmented and niche with key players operating in this industry. It is observed that key players offering different types of applications. Major companies are focused on in-orbit servicing, debris removal, and refueling technologies. A company Astroscale recently launched the ELSA-d mission to demonstrate key technologies for debris removal and in-orbit servicing. It has partnerships with JAXA and other organizations have helped it establish a strong position. The top five players in the industry are Northrop Grumman Corporation, Orbit Fab, Astroscale, Clear Space, Obruta Space Solutions Corporation.
List of Top Space In-Orbit Refueling Companies:
- Astroscale (Japan)
- Orbit Fab (U.S.)
- Clear Space (Switzerland)
- Obruta Space Solutions (Canada)
- D-Orbit SpA (Italy)
- Maxar Technologies (U.S.)
- Eta Space (U.S.)
KEY INDUSTRY DEVELOPMENTS:
- October 2023: NASA announced plans to collaborate with commercial partners to develop in-orbit refueling capabilities for the Gateway, a lunar outpost for Artemis missions. This initiative aimed to demonstrate the feasibility of refueling spacecraft in lunar orbit to support sustainable lunar exploration.
- June 2023: Northrop Grumman's Mission Extension Vehicle (MEV) successfully completed its second mission by docking with another satellite in geostationary orbit and extending its operational life. This demonstrates the capability of in-orbit servicing for maintaining and extending the lifespan of operational satellites.
- June 2023: Aerojet Rocketdyne announces successful testing of a new propulsion system designed for in-orbit refueling missions. The advancements aim to improve propellant efficiency and reliability, supporting future satellite servicing and exploration missions
- March 2023: SpaceX unveiled plans to integrate refuelling capabilities into its Starship spacecraft, enabling multiple refuelling missions to support crewed lunar landings and deep space missions. This development underscores the role of in-space refuelling in achieving ambitious space exploration goals.
- December 2022: Airbus Defence and Space announced a partnership with ESA (European Space Agency) to develop advanced electric propulsion systems for satellite refuelling missions. The collaboration aimed to combine ESA's expertise in propulsion technologies with Airbus's capabilities in spacecraft manufacturing and operations
REPORT COVERAGE
The report provides detailed information on the competitive market landscape and focuses on leading companies, product types, and leading product applications. Besides this, the report offers insights into the space in-orbit refueling market trends and highlights key industry developments. In addition to the above factors, it contains several factors that have contributed to the sizing of the global space in-orbit refueling market in recent years.
Request for Customization to gain extensive market insights.
Report Scope & Segmentation
|
ATTRIBUTE |
DETAILS |
|
Study Period |
2019-2032 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Estimated Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024-2032 |
|
Historical Period |
2019-2022 |
|
Growth Rate |
CAGR of 12.4% from 2024 to 2032 |
|
Unit |
Value (USD Million) |
|
Segmentation |
By Propellant
|
|
By Operation
|
|
|
By Platform
|
|
|
By Region
|
Frequently Asked Questions
The market was valued at USD 1,171.1 million in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 3,298.5 million in 2032.
Global market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12.4%.
By operation, the refueling segment dominated this market.
The top players in the industry are Northrop Grumman Corporation, Orbit Fab, Astroscale, Clear Space, Obruta Space Solutions Corporation.
North America captured the highest market share in 2023.
Related Reports
-
US +1 833 909 2966 ( Toll Free )
-
Get In Touch With Us


